查找算法之——二叉查找树(图文分析)
一、数据结构
二叉查找树基于二叉树,每个节点储存着键和值,以及指向左右子树的链接,一颗二叉查找树代表了一组键值对的集合,类似于python中的字典(字典中的键值对储存是无序的)。在这里我们规定节点左子树中的节点的键都小于它,右子树中的节点都大于它,如果我们将所有节点向下投影到一条线上,可以得到一条有序的序列。

二、主要方法(默认为递归实现)
部分方法的迭代实现在末尾展示
1、查找和排序
在符号表中查找一个键,从根节点开始,如果节点的键和被查找的键相等,就返回节点的值,如果节点的值大于被查找的键的值,就在节点的左子树中查找,反之在右子树中查找,直到节点为空或查找命中。如果键在符号表中则查找命中,返回键对应的值,如果键不在符号表中则未命中,返回null(null为指向一个它可能会存在的空节点的链接)
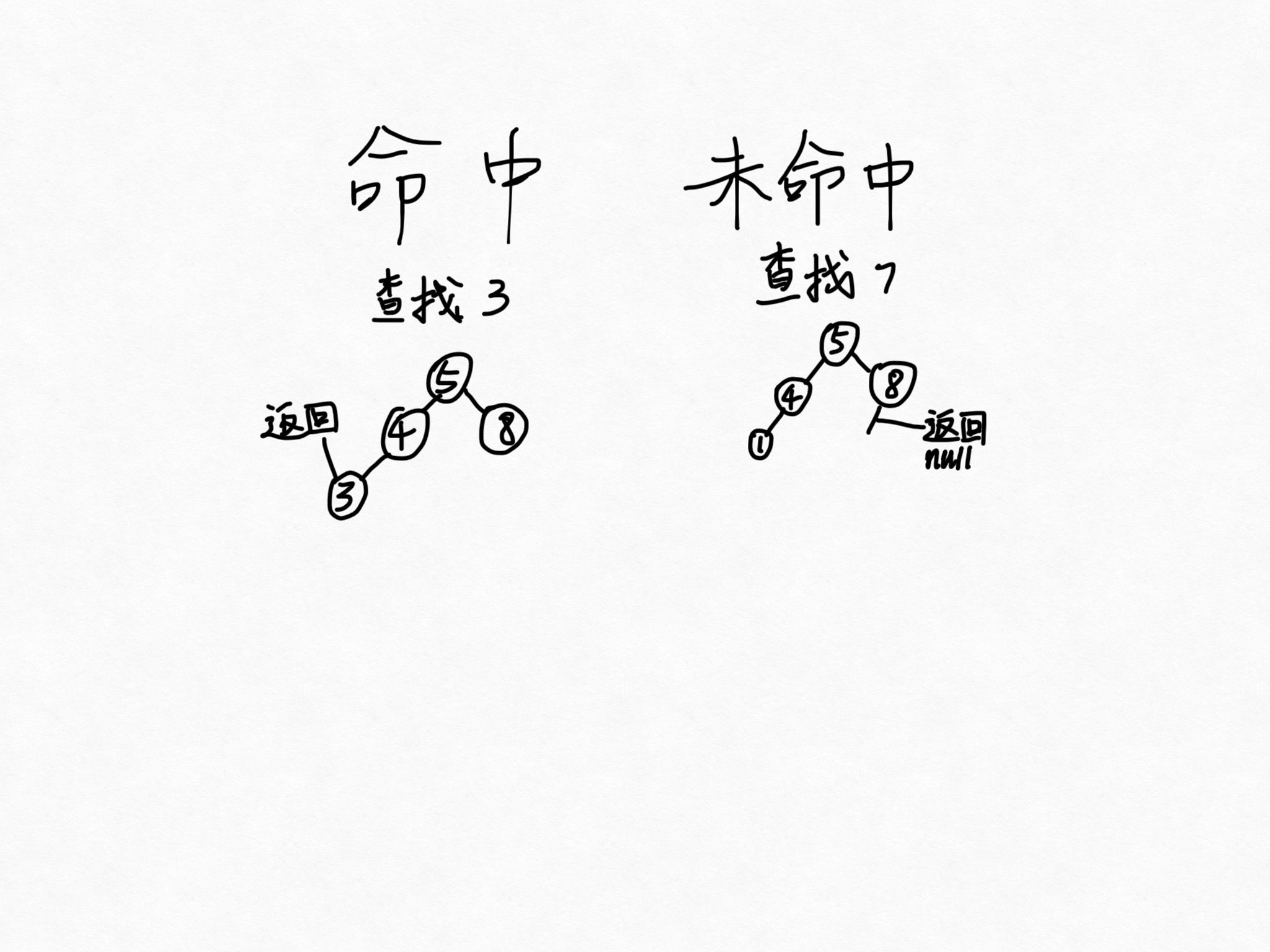
在上一篇结尾处引入的方法有许多都用到了这个算法:
1 public Value get(Key key) {// 通过键从符号表中获取对应的值,返回键key对应的值
2 return get(root, key);
3 }
4
5 private Value get(Node x, Key key) {// 递归
6 if (key == null) {
7 return null;
8 }
9 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
10 if (cmp < 0) {
11 return get(x.left, key);
12 } else if (cmp > 0) {
13 return get(x.right, key);
14 } else
15 return x.val;
16 }
17
18
19 public void put(Key key, Value val) {//修改或添加节点
20 root = put(root, key, val);
21 }
22
23 private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
24 if (x == null) {// 创建新节点
25 return new Node(key, val, 1);
26 }
27 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
28 if (cmp < 0) {
29 x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
30 } else if (cmp > 0) {
31 x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
32 } else {
33 x.val = val;
34 }
35 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
36 return x;// 在插入结束时返回(更新节点的相关信息)
37 }
其中的size()方法表示以节点为根节点的子树的节点数:
1 public int size() {
2 return size(root);
3 }
4
5 private int size(Node x) {
6 if (x != null) {
7 return x.N;
8 } else {
9 return 0;
10 }
11 }
size()的递归实现需要理解其运行细节
由于是递归实现,代码第35将会从查找经过的路径由下至上,更新每个节点计数器的值。
在最坏情况下,一颗有n个节点的二叉树到根节点的距离为n,最好情况下,每条空链接和根节点的距离都为lgN。大家可以想象一下这两种情况下树的样子。
下面请读者思考用递归的形式完成查找最小键和在树中查找小于等于key的最大键两个方法。
1 public Key min() {
2 return min(root).key;
3 }
4 public Node min(Node x) {
5 if(x.left==null) {
6 return x;
7 }else {
8 return min(x.left);
9 }
10 }
1 public Key floor(Key key) {
2 Node x== floor(root,key);
3 if(x==null) {
4 return null;
5 }else {
6 return x.key;
7 }
8 }
9
10 public Node floor(Node x,key) {
11 if (x == null) {
12 return null;
13 }
14 int cmp=key.compareto(x.key);
15 if(cmp<0) {
16 return floor(x.left,key);
17 }
18 Node t=floor(x.right,key);
19 if(t!=null) {
20 return t;
21 }else {
22 return x;
23 }
24 }
与之相反的max和ceiling(返回大于等于key的最小键)方法,实现原理相同。请读者当做练习实现,参考最后的代码展示。
2、排名
下面我们将要实现两个重要的方法,rank和select,select方法的参数是一个整型,他将返回排名为这个整型的键,而rank和select相反,参数为一个键,返回的是这个键的排名。
select和rank是在size的基础上实现的。
1 public Key select(int k) {// 返回排名为k的键
2 return select(root, k).key;
3 }
4
5 private Node select(Node x, int k) {// 返回排名为k的节点
6 if (x == null) {
7 return null;
8 }
9 int t = size(x.left);
10 if (t > k) {
11 return select(x.left, k);
12 } else if (t < k) {
13 return select(x.right, k - t - 1);
14 } else {
15 return x;
16 }
17 }
1 public int rank(Key key) {// 返回key的排名
2 return rank(key, root);
3 }
4
5 private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
6 if (key == null) {
7 return 0;
8 }
9 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
10 if (cmp < 0) {
11 return rank(key, x.left);
12 } else if (cmp > 0) {
13 return rank(key, x.right) + size(x.left) + 1;//注意体会这个+1
14 } else {
15 return size(x.left);
16 }
17 }
rank和put有点像,都是先不断比较确定键的位置,不过rank返回的是下一次的递归加上已经确定的排名。
3、删除
deleteMin为删除最小节点,任何情况下,最小节点只可能有右子树,所以在执行操作时只需将被最小节点的右节点代替最小节点即可。(删除最大节点与此类似)

1 public void deleteMin() {
2 root = deleteMin(root);
3 }
4
5 private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
6 if (x.left == null) {
7 return x.right;
8 }
9 x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
10 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;//由于删除操作,所以需要更新路径上节点的计数器
11 return x;// 在删除结束后返回节点的相关信息
12 }
请体会这里第10、11行代码,理解运行细节
分析:返回和传入相同,例如deleteMin(x),最后返回的将是x节点,但此时节点包含的信息已经改变,因为要更新x.N,实际运行会从被删除节点的上一个节点开始,由下至上进行更新,需要确定的是,删除和返回操作都是在同一条路径上进行的,没经过的路径将保持不变。
如果被删除的节点左右节点都存在,操作将变得复杂,这里给出一种经典的方案(但还不是最好)。
找到要删除的节点,接着用节点右子树的最小节点代替它,最后给新节点接上左右链接。
在这里我们会用到min方法来找到右子树的最小节点,再用deleteMin方法来删除右子树中的最小节点,同时把deleteMin方法的返回值传给新节点的右链接。

结合图中流程和代码更容易理解
1 public void delete(Key key) {
2 root = delete(root, key);
3 }
4
5 private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
6 if (x == null) {
7 return null;
8 }
9 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
10 if (cmp > 0) {
11 x.right = delete(x.right, key);
12 } else if (cmp < 0) {
13 x.left = delete(x.left, key);
14 } else {// 找到key
15 if (x.right == null) {// 无右子树 将左子树接上
16 return x.left;
17 }
18 if (x.left == null) {
19 return x.right;
20 }
21 Node t = x;
22 // **********************************************
23 x = min(t.right); // *被删除节点有左右子树,用右子树中的最小节点代替它
24 x.left = t.left; // *替换后,左子树保持不变
25 x.right = deleteMin(t.right); // *右子树删除最小节点后再接入
26 // **********************************************
27 }
28 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;// 更新新节点和上一个节点的n
29 return x;// 不一定会用到
30 }
4、范围查找
范围查找即返回指定范围内的所有键,这需要我们遍历二叉树,在这里我们使用中序遍历,将会得到一组由小到大的序列。
在这之前先来看看怎么怎么将二叉树查找树中的所有键由小到大打印出来:
1 private void print(Node x) {//x为树的根节点
2 if(x==null) {
3 return;
4 }
5 print(x.left);
6 System.out.println(x.key);
7 print(x.right);;
8 }
在范围查找中我们将传入两个参数lo和hi来确定范围,并将范围内的键存入队列,最后返回队列。
1 public Iterable<Key> keys() {// 返回查找二叉树中的所有键
2 return keys(min(), max());
3 }
4 public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {// 二叉树的范围查找操作
5 Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();
6 keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
7 return queue;
8 }
9
10 private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
11 if (x == null) {
12 return;
13 }
14 int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
15 int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
16 // 三个if类似于中序遍历
17 if (cmplo < 0) {
18 keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
19 }
20 if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) {
21 queue.enqueue(x.key);
22 }
23 if (cmphi > 0) {
24 keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
25 }
26 }
对于递归和非递归,有人证实在一般情况下非递归的效率更高,如果树不是平衡的,函数调用栈的深度可能会出现问题。递归形式能让人更容易理解,通过实现再非递归理解代码的本质。
三、代码展示(包含所有代码及非递归实现)
1 package Unit3; 2 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue; 6 7 public class BST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {// 二叉查找树 8 private Node root;// 查找二叉树的根节点 9 10 private class Node { 11 private Key key;// 键 12 private Value val;// 值 13 private Node left, right;// 指向子树的链接 14 private int N;// 以该节点为根节点的子树中的总节点数 15 16 public Node(Key key, Value val, int N) { 17 this.key = key; 18 this.val = val; 19 this.N = N; 20 } 21 } 22 23 public int size() { 24 return size(root); 25 } 26 27 private int size(Node x) { 28 if (x != null) { 29 return x.N; 30 } else { 31 return 0; 32 } 33 } 34 35 public Value get(Key key) {// 返回键key对应的值 36 return get(root, key); 37 } 38 39 private Value get(Node x, Key key) {// 递归 40 if (key == null) { 41 return null; 42 } 43 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 44 if (cmp < 0) { 45 return get(x.left, key); 46 } else if (cmp > 0) { 47 return get(x.right, key); 48 } else 49 return x.val; 50 } 51 52 /* 53 * private Value getTwo(Node x, Key key) {// 非递归 if (key == null) { return null; 54 * } int cmp; while (x != null) { cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); if (cmp < 0) { x = 55 * x.left; } else if (cmp > 0) { x = x.right; } else return x.val; } return 56 * null; } 57 */ 58 59 public void put(Key key, Value val) { 60 root = put(root, key, val); 61 } 62 63 private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) { 64 if (x == null) {// 创建新节点 65 return new Node(key, val, 1); 66 } 67 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 68 if (cmp < 0) { 69 x.left = put(x.left, key, val); 70 } else if (cmp > 0) { 71 x.right = put(x.right, key, val); 72 } else { 73 x.val = val; 74 } 75 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 76 return x;// 在插入结束时返回(更新节点的相关信息) 77 } 78 79 private Node putTwo(Node x, Key key, Value val) {// 在存在基本操作基础上的非递归put() 80 if (get(key) != null) { 81 select(root, rank(key)).val = val; 82 } 83 return x; 84 } 85 86 public Key min() { 87 return min(root).key; 88 } 89 90 private Node min(Node x) { 91 if (x.left == null) { 92 return x; 93 } 94 return min(x.left); 95 } 96 97 public Key max() { 98 return max(root).key; 99 } 100 101 private Node max(Node x) { 102 if (x.right == null) { 103 return x; 104 } 105 return min(x.right); 106 } 107 108 public Key floor(Key key) { 109 Node x = floor(root, key); 110 if (x == null) { 111 return null; 112 } 113 return x.key; 114 } 115 116 // private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {//测试(个人思路 117 // if(x==null) { 118 // return null; 119 // } 120 // int cmp=key.compareTo(x.key); 121 // if(cmp<0) { 122 // return floor(x.left,key); 123 // }else if(cmp>0) { 124 // if(x.right==null) { 125 // return x.right; 126 // } 127 // return floor(x.right,key); 128 // } 129 // else { 130 // return x; 131 // } 132 // } 133 134 private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {// 类似前序遍历 找到后不再执行后续操作 135 if (x == null) { 136 return null; 137 } 138 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 139 if (cmp == 0) { 140 return x; 141 } 142 if (cmp < 0) { 143 return floor(x.left, key); 144 } 145 Node f = floor(x.right, key); 146 if (f != null) { 147 return f; 148 } else { 149 return x; 150 } 151 } 152 153 public Key ceiling(Key key) { 154 Node x = ceiling(root, key); 155 if (x == null) { 156 return null; 157 } 158 return x.key; 159 } 160 161 private Node ceiling(Node x, Key key) { 162 if (x == null) { 163 return null; 164 } 165 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 166 if (cmp == 0) { 167 return x; 168 } 169 if (cmp > 0) {// 往大找 170 return ceiling(x.right, key); 171 } 172 Node f = floor(x.left, key); 173 if (f != null) { 174 return f; 175 } else { 176 return x; 177 } 178 } 179 180 public Key FOC(Key key, String s) {// 合并两个方法(自创 181 Node x = null; 182 if (s.equals("floor")) { 183 x = floor(root, key); 184 } else if (s.equals("ceiling")) { 185 x = ceiling(root, key); 186 } else { 187 System.out.println("输入错误!将返回null"); 188 } 189 if (x == null) { 190 return null; 191 } 192 return x.key; 193 } 194 195 public Key select(int k) {// 返回排名为k的键 196 return select(root, k).key; 197 } 198 199 public Node select(Node x, int k) {// 返回排名为k的节点 200 if (x == null) { 201 return null; 202 } 203 int t = size(x.left); 204 if (t > k) { 205 return select(x.left, k); 206 } else if (t < k) { 207 return select(x.right, k - t - 1); 208 } else { 209 return x; 210 } 211 } 212 213 public Node selectTwo(Node x, int k) { 214 if (x == null) { 215 return null; 216 } 217 while (k != size(x.left)) { 218 if (size(x.left) > k) { 219 x = x.left; 220 } else { 221 x = x.right; 222 k = k - size(x.left) - 1; 223 } 224 } 225 return x; 226 } 227 228 public int rank(Key key) {// 返回key的排名 229 return rank(key, root); 230 } 231 232 private int rank(Key key, Node x) { 233 if (key == null) { 234 return 0; 235 } 236 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 237 if (cmp < 0) { 238 return rank(key, x.left); 239 } else if (cmp > 0) { 240 return rank(key, x.right) + size(x.left) + 1; 241 } else { 242 return size(x.left); 243 } 244 } 245 246 public void deleteMin() { 247 root = deleteMin(root); 248 } 249 250 private Node deleteMin(Node x) { 251 if (x.left == null) { 252 return x.right; 253 } 254 x.left = deleteMin(x.left); 255 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1; 256 return x;// 在删除结束后返回节点的相关信息 257 } 258 259 public void delete(Key key) { 260 root = delete(root, key); 261 } 262 263 private Node delete(Node x, Key key) { 264 if (x == null) { 265 return null; 266 } 267 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 268 if (cmp > 0) { 269 x.right = delete(x.right, key); 270 } else if (cmp < 0) { 271 x.left = delete(x.left, key); 272 } else {// 找到key 273 if (x.right == null) {// 无右子树 将左子树接上 274 return x.left; 275 } 276 if (x.left == null) { 277 return x.right; 278 } 279 Node t = x; 280 // ********************************************** 281 x = min(t.right); // *被删除节点有左右子树,用右子树中的最小节点代替它 282 x.left = t.left; // *替换后,左子树保持不变 283 x.right = deleteMin(t.right); // *右子树删除最小节点后再接入 284 // ********************************************** 285 } 286 x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;// 更新新节点和上一个节点的n 287 return x;// 不一定会用到 288 } 289 290 private void print(Node x) {//x为树的根节点 291 if(x==null) { 292 return; 293 } 294 print(x.left); 295 System.out.println(x.key); 296 print(x.right);; 297 } 298 299 public Iterable<Key> keys() {// 返回查找二叉树中的所有键 300 return keys(min(), max()); 301 } 302 303 public Iterable<Key> keysTwo() {// 范围查找非递归方法 304 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack(); 305 Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>(); 306 Node x = root; 307 while (x != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {// 中序遍历非递减 308 if (x != null) { 309 stack.add(x); 310 x = x.left; 311 } else { 312 x = stack.pop(); 313 queue.enqueue(x.key); 314 x = x.right; 315 } 316 } 317 /* 318 * while(x!=null||stack.isEmpty()) {// 中序遍历非递增 if(x!=null) { stack.add(x); 319 * x=x.right; }else { x=stack.pop(); queue.enqueue(x.key); x=x.left; } } 320 */ 321 return queue;// 返回非降序队列 322 } 323 324 public Iterable<Key> keysThree(int i) {// 范围查找非递归方法(包含前中序遍历) 325 Stack<Node> stack = new Stack(); 326 Queue<Key> queue1 = new Queue<Key>();// 保存前序遍历 327 Queue<Key> queue2 = new Queue<Key>();// 保存中序遍历 328 Node x = root; 329 while (x != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { 330 for (; x != null; x = x.left) { 331 stack.add(x); 332 queue1.enqueue(x.key);// 前序遍历 333 } 334 for (; x == null && !stack.isEmpty(); x = x.right) { 335 x = stack.pop(); 336 queue2.enqueue(x.key);// 中序遍历 337 } 338 } 339 if (i == 1) { 340 return queue1; 341 } 342 return queue2; 343 } 344 345 public Iterable<Key> keysFour() {// 范围查找非递归方法(后序遍历) 346 Stack<Node> stackA = new Stack(); 347 Stack<Node> stackB = new Stack(); 348 Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>();// 保存后序遍历 349 Node x = root; 350 while (x != null || !stackB.isEmpty()) { 351 for (; x != null; x = x.right) { 352 stackA.add(x); 353 stackB.add(x); 354 } 355 for (; x == null && !stackB.isEmpty(); x = x.left) { 356 x = stackB.pop(); 357 } 358 } 359 360 while (!stackA.isEmpty()) { 361 queue.enqueue(stackA.pop().key); 362 } 363 return queue; 364 } 365 366 public Iterable<Key> keys(Key lo, Key hi) {// 二叉树的范围查找操作 367 Queue<Key> queue = new Queue<Key>(); 368 keys(root, queue, lo, hi); 369 return queue; 370 } 371 372 private void keys(Node x, Queue<Key> queue, Key lo, Key hi) { 373 if (x == null) { 374 return; 375 } 376 int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key); 377 int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key); 378 // 三个if类似于中序遍历 379 if (cmplo < 0) { 380 keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi); 381 } 382 if (cmplo <= 0 && cmphi >= 0) { 383 queue.enqueue(x.key); 384 } 385 if (cmphi > 0) { 386 keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi); 387 } 388 } 389 390 public static void main(String[] args) { 391 BST<Integer, String> bst = new BST<Integer, String>(); 392 bst.put(5, "one"); 393 bst.put(4, "two"); 394 bst.put(2, "one"); 395 bst.put(6, "two"); 396 bst.put(3, "one"); 397 for (Integer x : bst.keysFour()) {// 中序遍历 398 System.out.println(x + " " + bst.get(x)); 399 } 400 // bst.delete(2); 401 } 402 }



